Data Structures - Circular Queue
Why was the concept of the circular queue introduced?
There was one limitation in the array implementation of Queue. If the rear reaches to the end position of the Queue then there might be possibility that some vacant spaces are left in the beginning which cannot be utilized. So, to overcome such limitations, the concept of the circular queue was introduced.
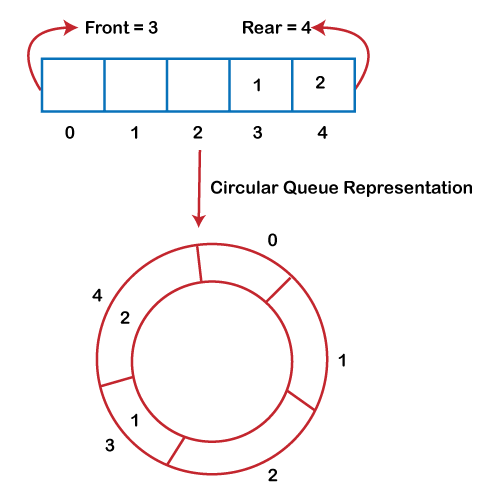
As we can see in the above image, the rear is at the last position of the Queue and front is pointing somewhere rather than the 0th position. In the above array, there are only two elements and other three positions are empty. The rear is at the last position of the Queue; if we try to insert the element then it will show that there are no empty spaces in the Queue. There is one solution to avoid such wastage of memory space by shifting both the elements at the left and adjust the front and rear end accordingly. It is not a practically good approach because shifting all the elements will consume lots of time. The efficient approach to avoid the wastage of the memory is to use the circular queue data structure.
What is a Circular Queue?
A circular queue is similar to a linear queue as it is also based on the FIFO (First In First Out) principle except that the last position is connected to the first position in a circular queue that forms a circle. It is also known as a Ring Buffer.
Operations on Circular Queue
The following are the operations that can be performed on a circular queue:
- Front: It is used to get the front element from the Queue.
- Rear: It is used to get the rear element from the Queue.
- enQueue(value): This function is used to insert the new value in the Queue. The new element is always inserted from the rear end.
- deQueue(): This function deletes an element from the Queue. The deletion in a Queue always takes place from the front end.
Applications of Circular Queue
The circular Queue can be used in the following scenarios:
- Memory management: The circular queue provides memory management. As we have already seen that in linear queue, the memory is not managed very efficiently. But in case of a circular queue, the memory is managed efficiently by placing the elements in a location which is unused.
- CPU Scheduling: The operating system also uses the circular queue to insert the processes and then execute them.
- Traffic system: In a computer-control traffic system, traffic light is one of the best examples of the circular queue. Each light of traffic light gets ON one by one after every jinterval of time. Like red light gets ON for one minute then yellow light for one minute and then green light. After green light, the red light gets ON.
Enqueue operation
The steps of enqueue operation are given below:
- First, we will check whether the Queue is full or not.
- Initially the front and rear are set to -1. When we insert the first element in a Queue, front and rear both are set to 0.
- When we insert a new element, the rear gets incremented, i.e., rear=rear+1.
Comments
Post a Comment